Designing and Training a Fully Attentive Multimodal Transformer Network for Medical Visual Question Answering Task
Team: Md Mesbahur Rahman
Resources: [Technical report]
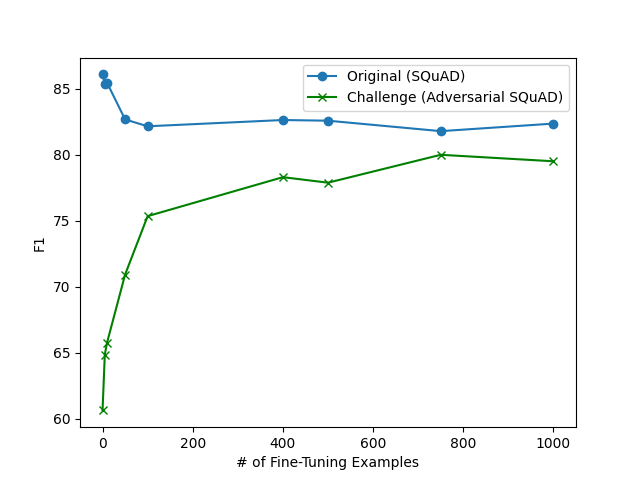
Summary: Medical Question Answering is a very important and impactful application of Multi-modal learning. It can contribute to the interpretability of machine learning model in medical applications, reduce workload of medical professional, and can be a part of fully automated healthcare system. In this project, we have done a background research on the state of the art of Medical Visual Question Answering research. Based on some latest well performing paper, we propose our own fully attention based Transformer only network for solving the medical visual question answering task by treating a multi-class classification problem. We also present some analysis on hyperparameter tuning of the model, compare its performance with models from some other notable papers and suggest some future improvements of our model.
My contribution: Conducted background research on the state of the art of Medical Visual Question Answering research. Based on some latest well performing paper, proposed a novel fully attention-based Transformer only network for solving the medical visual question answering task by treating a multi-class classification problem. Trained the proposed model on the train set of VQA-RAD dataset and our model showed encouraging result on the test-set of the VQA dataset. Also presented some analysis on hyperparameter tuning of the model, compared its performance with models from some other notable papers and suggested some future improvements of our model including steps like pre-training the model on much larger medical vision language datasets.